Classic ML Models¶
This module implements classic machine learning models in PyTorch Lightning, including linear regression and logistic regression. Unlike other libraries that implement these models, here we use PyTorch to enable multi-GPU, multi-TPU and half-precision training.
Note
We rely on the community to keep these updated and working. If something doesn’t work, we’d really appreciate a contribution to fix!
Linear Regression¶
Linear regression fits a linear model between a real-valued target variable 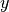 and one or more features
and one or more features 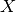 . We
estimate the regression coefficients that minimize the mean squared error between the predicted and true target
values.
. We
estimate the regression coefficients that minimize the mean squared error between the predicted and true target
values.
We formulate the linear regression model as a single-layer neural network. By default we include only one neuron in the output layer, although you can specify the output_dim yourself.
Add either L1 or L2 regularization, or both, by specifying the regularization strength (default 0).
from pl_bolts.models.regression import LinearRegression
import pytorch_lightning as pl
from pl_bolts.datamodules import SklearnDataModule
from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes
X, y = load_diabetes(return_X_y=True)
loaders = SklearnDataModule(X, y)
model = LinearRegression(input_dim=10)
trainer = pl.Trainer()
trainer.fit(model, train_dataloaders=loaders.train_dataloader(), val_dataloaders=loaders.val_dataloader())
trainer.test(test_dataloaders=loaders.test_dataloader())
- class pl_bolts.models.regression.linear_regression.LinearRegression(input_dim, output_dim=1, bias=True, learning_rate=0.0001, optimizer=<class 'torch.optim.adam.Adam'>, l1_strength=0.0, l2_strength=0.0, **kwargs)[source]
Bases:
LightningModuleWarning
The feature LinearRegression is currently marked under review. The compatibility with other Lightning projects is not guaranteed and API may change at any time. The API and functionality may change without warning in future releases. More details: https://lightning-bolts.readthedocs.io/en/latest/stability.html
Linear regression model implementing - with optional L1/L2 regularization $$min_{W} ||(Wx + b) - y ||_2^2 $$
- Parameters:
- configure_optimizers()[source]
Choose what optimizers and learning-rate schedulers to use in your optimization. Normally you’d need one. But in the case of GANs or similar you might have multiple.
- Return type:
- Returns:
Any of these 6 options.
Single optimizer.
List or Tuple of optimizers.
Two lists - The first list has multiple optimizers, and the second has multiple LR schedulers (or multiple
lr_scheduler_config).Dictionary, with an
"optimizer"key, and (optionally) a"lr_scheduler"key whose value is a single LR scheduler orlr_scheduler_config.Tuple of dictionaries as described above, with an optional
"frequency"key.None - Fit will run without any optimizer.
The
lr_scheduler_configis a dictionary which contains the scheduler and its associated configuration. The default configuration is shown below.lr_scheduler_config = { # REQUIRED: The scheduler instance "scheduler": lr_scheduler, # The unit of the scheduler's step size, could also be 'step'. # 'epoch' updates the scheduler on epoch end whereas 'step' # updates it after a optimizer update. "interval": "epoch", # How many epochs/steps should pass between calls to # `scheduler.step()`. 1 corresponds to updating the learning # rate after every epoch/step. "frequency": 1, # Metric to to monitor for schedulers like `ReduceLROnPlateau` "monitor": "val_loss", # If set to `True`, will enforce that the value specified 'monitor' # is available when the scheduler is updated, thus stopping # training if not found. If set to `False`, it will only produce a warning "strict": True, # If using the `LearningRateMonitor` callback to monitor the # learning rate progress, this keyword can be used to specify # a custom logged name "name": None, }
When there are schedulers in which the
.step()method is conditioned on a value, such as thetorch.optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateauscheduler, Lightning requires that thelr_scheduler_configcontains the keyword"monitor"set to the metric name that the scheduler should be conditioned on.# The ReduceLROnPlateau scheduler requires a monitor def configure_optimizers(self): optimizer = Adam(...) return { "optimizer": optimizer, "lr_scheduler": { "scheduler": ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, ...), "monitor": "metric_to_track", "frequency": "indicates how often the metric is updated" # If "monitor" references validation metrics, then "frequency" should be set to a # multiple of "trainer.check_val_every_n_epoch". }, } # In the case of two optimizers, only one using the ReduceLROnPlateau scheduler def configure_optimizers(self): optimizer1 = Adam(...) optimizer2 = SGD(...) scheduler1 = ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer1, ...) scheduler2 = LambdaLR(optimizer2, ...) return ( { "optimizer": optimizer1, "lr_scheduler": { "scheduler": scheduler1, "monitor": "metric_to_track", }, }, {"optimizer": optimizer2, "lr_scheduler": scheduler2}, )
Metrics can be made available to monitor by simply logging it using
self.log('metric_to_track', metric_val)in yourLightningModule.Note
The
frequencyvalue specified in a dict along with theoptimizerkey is an int corresponding to the number of sequential batches optimized with the specific optimizer. It should be given to none or to all of the optimizers. There is a difference between passing multiple optimizers in a list, and passing multiple optimizers in dictionaries with a frequency of 1:In the former case, all optimizers will operate on the given batch in each optimization step.
In the latter, only one optimizer will operate on the given batch at every step.
This is different from the
frequencyvalue specified in thelr_scheduler_configmentioned above.def configure_optimizers(self): optimizer_one = torch.optim.SGD(self.model.parameters(), lr=0.01) optimizer_two = torch.optim.SGD(self.model.parameters(), lr=0.01) return [ {"optimizer": optimizer_one, "frequency": 5}, {"optimizer": optimizer_two, "frequency": 10}, ]
In this example, the first optimizer will be used for the first 5 steps, the second optimizer for the next 10 steps and that cycle will continue. If an LR scheduler is specified for an optimizer using the
lr_schedulerkey in the above dict, the scheduler will only be updated when its optimizer is being used.Examples:
# most cases. no learning rate scheduler def configure_optimizers(self): return Adam(self.parameters(), lr=1e-3) # multiple optimizer case (e.g.: GAN) def configure_optimizers(self): gen_opt = Adam(self.model_gen.parameters(), lr=0.01) dis_opt = Adam(self.model_dis.parameters(), lr=0.02) return gen_opt, dis_opt # example with learning rate schedulers def configure_optimizers(self): gen_opt = Adam(self.model_gen.parameters(), lr=0.01) dis_opt = Adam(self.model_dis.parameters(), lr=0.02) dis_sch = CosineAnnealing(dis_opt, T_max=10) return [gen_opt, dis_opt], [dis_sch] # example with step-based learning rate schedulers # each optimizer has its own scheduler def configure_optimizers(self): gen_opt = Adam(self.model_gen.parameters(), lr=0.01) dis_opt = Adam(self.model_dis.parameters(), lr=0.02) gen_sch = { 'scheduler': ExponentialLR(gen_opt, 0.99), 'interval': 'step' # called after each training step } dis_sch = CosineAnnealing(dis_opt, T_max=10) # called every epoch return [gen_opt, dis_opt], [gen_sch, dis_sch] # example with optimizer frequencies # see training procedure in `Improved Training of Wasserstein GANs`, Algorithm 1 # https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.00028 def configure_optimizers(self): gen_opt = Adam(self.model_gen.parameters(), lr=0.01) dis_opt = Adam(self.model_dis.parameters(), lr=0.02) n_critic = 5 return ( {'optimizer': dis_opt, 'frequency': n_critic}, {'optimizer': gen_opt, 'frequency': 1} )
Note
Some things to know:
Lightning calls
.backward()and.step()on each optimizer as needed.If learning rate scheduler is specified in
configure_optimizers()with key"interval"(default “epoch”) in the scheduler configuration, Lightning will call the scheduler’s.step()method automatically in case of automatic optimization.If you use 16-bit precision (
precision=16), Lightning will automatically handle the optimizers.If you use multiple optimizers,
training_step()will have an additionaloptimizer_idxparameter.If you use
torch.optim.LBFGS, Lightning handles the closure function automatically for you.If you use multiple optimizers, gradients will be calculated only for the parameters of current optimizer at each training step.
If you need to control how often those optimizers step or override the default
.step()schedule, override theoptimizer_step()hook.
- forward(x)[source]
Same as
torch.nn.Module.forward().
- test_epoch_end(outputs)[source]
Called at the end of a test epoch with the output of all test steps.
# the pseudocode for these calls test_outs = [] for test_batch in test_data: out = test_step(test_batch) test_outs.append(out) test_epoch_end(test_outs)
- Parameters:
outputs¶ (
List[Dict[str,Tensor]]) – List of outputs you defined intest_step_end(), or if there are multiple dataloaders, a list containing a list of outputs for each dataloader- Return type:
- Returns:
None
Note
If you didn’t define a
test_step(), this won’t be called.Examples
With a single dataloader:
def test_epoch_end(self, outputs): # do something with the outputs of all test batches all_test_preds = test_step_outputs.predictions some_result = calc_all_results(all_test_preds) self.log(some_result)
With multiple dataloaders, outputs will be a list of lists. The outer list contains one entry per dataloader, while the inner list contains the individual outputs of each test step for that dataloader.
def test_epoch_end(self, outputs): final_value = 0 for dataloader_outputs in outputs: for test_step_out in dataloader_outputs: # do something final_value += test_step_out self.log("final_metric", final_value)
- test_step(batch, batch_idx)[source]
Operates on a single batch of data from the test set. In this step you’d normally generate examples or calculate anything of interest such as accuracy.
# the pseudocode for these calls test_outs = [] for test_batch in test_data: out = test_step(test_batch) test_outs.append(out) test_epoch_end(test_outs)
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Any of.
Any object or value
None- Testing will skip to the next batch
# if you have one test dataloader: def test_step(self, batch, batch_idx): ... # if you have multiple test dataloaders: def test_step(self, batch, batch_idx, dataloader_idx=0): ...
Examples:
# CASE 1: A single test dataset def test_step(self, batch, batch_idx): x, y = batch # implement your own out = self(x) loss = self.loss(out, y) # log 6 example images # or generated text... or whatever sample_imgs = x[:6] grid = torchvision.utils.make_grid(sample_imgs) self.logger.experiment.add_image('example_images', grid, 0) # calculate acc labels_hat = torch.argmax(out, dim=1) test_acc = torch.sum(y == labels_hat).item() / (len(y) * 1.0) # log the outputs! self.log_dict({'test_loss': loss, 'test_acc': test_acc})
If you pass in multiple test dataloaders,
test_step()will have an additional argument. We recommend setting the default value of 0 so that you can quickly switch between single and multiple dataloaders.# CASE 2: multiple test dataloaders def test_step(self, batch, batch_idx, dataloader_idx=0): # dataloader_idx tells you which dataset this is. ...
Note
If you don’t need to test you don’t need to implement this method.
Note
When the
test_step()is called, the model has been put in eval mode and PyTorch gradients have been disabled. At the end of the test epoch, the model goes back to training mode and gradients are enabled.
- training_step(batch, batch_idx)[source]
Here you compute and return the training loss and some additional metrics for e.g. the progress bar or logger.
- Parameters:
batch¶ (
Tensor| (Tensor, …) | [Tensor, …]) – The output of yourDataLoader. A tensor, tuple or list.batch_idx¶ (
int) – Integer displaying index of this batchoptimizer_idx¶ (
int) – When using multiple optimizers, this argument will also be present.hiddens¶ (
Any) – Passed in iftruncated_bptt_steps> 0.
- Return type:
- Returns:
Any of.
Tensor- The loss tensordict- A dictionary. Can include any keys, but must include the key'loss'None- Training will skip to the next batch. This is only for automatic optimization.This is not supported for multi-GPU, TPU, IPU, or DeepSpeed.
In this step you’d normally do the forward pass and calculate the loss for a batch. You can also do fancier things like multiple forward passes or something model specific.
Example:
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx): x, y, z = batch out = self.encoder(x) loss = self.loss(out, x) return loss
If you define multiple optimizers, this step will be called with an additional
optimizer_idxparameter.# Multiple optimizers (e.g.: GANs) def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx, optimizer_idx): if optimizer_idx == 0: # do training_step with encoder ... if optimizer_idx == 1: # do training_step with decoder ...
If you add truncated back propagation through time you will also get an additional argument with the hidden states of the previous step.
# Truncated back-propagation through time def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx, hiddens): # hiddens are the hidden states from the previous truncated backprop step out, hiddens = self.lstm(data, hiddens) loss = ... return {"loss": loss, "hiddens": hiddens}
Note
The loss value shown in the progress bar is smoothed (averaged) over the last values, so it differs from the actual loss returned in train/validation step.
Note
When
accumulate_grad_batches> 1, the loss returned here will be automatically normalized byaccumulate_grad_batchesinternally.
- validation_epoch_end(outputs)[source]
Called at the end of the validation epoch with the outputs of all validation steps.
# the pseudocode for these calls val_outs = [] for val_batch in val_data: out = validation_step(val_batch) val_outs.append(out) validation_epoch_end(val_outs)
- Parameters:
outputs¶ (
List[Dict[str,Tensor]]) – List of outputs you defined invalidation_step(), or if there are multiple dataloaders, a list containing a list of outputs for each dataloader.- Return type:
- Returns:
None
Note
If you didn’t define a
validation_step(), this won’t be called.Examples
With a single dataloader:
def validation_epoch_end(self, val_step_outputs): for out in val_step_outputs: ...
With multiple dataloaders, outputs will be a list of lists. The outer list contains one entry per dataloader, while the inner list contains the individual outputs of each validation step for that dataloader.
def validation_epoch_end(self, outputs): for dataloader_output_result in outputs: dataloader_outs = dataloader_output_result.dataloader_i_outputs self.log("final_metric", final_value)
- validation_step(batch, batch_idx)[source]
Operates on a single batch of data from the validation set. In this step you’d might generate examples or calculate anything of interest like accuracy.
# the pseudocode for these calls val_outs = [] for val_batch in val_data: out = validation_step(val_batch) val_outs.append(out) validation_epoch_end(val_outs)
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Any object or value
None- Validation will skip to the next batch
# pseudocode of order val_outs = [] for val_batch in val_data: out = validation_step(val_batch) if defined("validation_step_end"): out = validation_step_end(out) val_outs.append(out) val_outs = validation_epoch_end(val_outs)
# if you have one val dataloader: def validation_step(self, batch, batch_idx): ... # if you have multiple val dataloaders: def validation_step(self, batch, batch_idx, dataloader_idx=0): ...
Examples:
# CASE 1: A single validation dataset def validation_step(self, batch, batch_idx): x, y = batch # implement your own out = self(x) loss = self.loss(out, y) # log 6 example images # or generated text... or whatever sample_imgs = x[:6] grid = torchvision.utils.make_grid(sample_imgs) self.logger.experiment.add_image('example_images', grid, 0) # calculate acc labels_hat = torch.argmax(out, dim=1) val_acc = torch.sum(y == labels_hat).item() / (len(y) * 1.0) # log the outputs! self.log_dict({'val_loss': loss, 'val_acc': val_acc})
If you pass in multiple val dataloaders,
validation_step()will have an additional argument. We recommend setting the default value of 0 so that you can quickly switch between single and multiple dataloaders.# CASE 2: multiple validation dataloaders def validation_step(self, batch, batch_idx, dataloader_idx=0): # dataloader_idx tells you which dataset this is. ...
Note
If you don’t need to validate you don’t need to implement this method.
Note
When the
validation_step()is called, the model has been put in eval mode and PyTorch gradients have been disabled. At the end of validation, the model goes back to training mode and gradients are enabled.
Logistic Regression¶
Logistic regression is a linear model used for classification, i.e. when we have a categorical target variable. This implementation supports both binary and multi-class classification.
In the binary case, we formulate the logistic regression model as a one-layer neural network with one neuron in the
output layer and a sigmoid activation function. In the multi-class case, we use a single-layer neural network but now
with 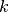 neurons in the output, where
neurons in the output, where 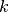 is the number of classes. This is also referred to as multinomial
logistic regression.
is the number of classes. This is also referred to as multinomial
logistic regression.
Add either L1 or L2 regularization, or both, by specifying the regularization strength (default 0).
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from pl_bolts.models.regression import LogisticRegression
from pl_bolts.datamodules import SklearnDataModule
import pytorch_lightning as pl
# use any numpy or sklearn dataset
X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
dm = SklearnDataModule(X, y)
# build model
model = LogisticRegression(input_dim=4, num_classes=3)
# fit
trainer = pl.Trainer(tpu_cores=8, precision=16)
trainer.fit(model, train_dataloaders=dm.train_dataloader(), val_dataloaders=dm.val_dataloader())
trainer.test(test_dataloaders=dm.test_dataloader(batch_size=12))
Any input will be flattened across all dimensions except the first one (batch). This means images, sound, etc… work out of the box.
# create dataset
dm = MNISTDataModule(num_workers=0, data_dir=tmpdir)
model = LogisticRegression(input_dim=28 * 28, num_classes=10, learning_rate=0.001)
model.prepare_data = dm.prepare_data
model.train_dataloader = dm.train_dataloader
model.val_dataloader = dm.val_dataloader
model.test_dataloader = dm.test_dataloader
trainer = pl.Trainer(max_epochs=2)
trainer.fit(model)
trainer.test(model)
# {test_acc: 0.92}
- class pl_bolts.models.regression.logistic_regression.LogisticRegression(input_dim, num_classes, bias=True, learning_rate=0.0001, optimizer=<class 'torch.optim.adam.Adam'>, l1_strength=0.0, l2_strength=0.0, **kwargs)[source]
Bases:
LightningModuleLogistic Regression Model.
Logistic Regression.
- Parameters:
- linear[source]
Linear layer.
- criterion[source]
Cross-Entropy loss function.
- optimizer[source]
Model optimizer to use.
- static add_model_specific_args(parent_parser)[source]
Adds model specific arguments to the parser.
- Parameters:
parent_parser¶ (
ArgumentParser) – Parent parser to which the arguments will be added.- Return type:
- Returns:
ArgumentParser with the added arguments.
- configure_optimizers()[source]
Configure the optimizer for the model.
- Return type:
- Returns:
Optimizer.
- forward(x)[source]
Forward pass of the model.
- test_epoch_end(outputs)[source]
Test epoch end for the model.
- test_step(batch, batch_idx)[source]
Test step for the model.
- training_step(batch, batch_idx)[source]
Training step for the model.
- validation_epoch_end(outputs)[source]
Validation epoch end for the model.
